Result
Data Catalog
Its importance and the challenges it presents
by Melanie Czink
In today’s data-driven business world, access to reliable, accurate, and understandable data is crucial for a company’s success. Data catalogs play a key role in supporting companies with regard to the organization, administration, and use of existing internal data records and assets. This innovative technology enables users to find data quickly and understand and apply it in order to make sound decisions. Despite the clear benefits offered by data catalogs, introducing them in an organization involves a range of challenges. This article explains why data catalogs are important, presents information on the experience six companies that introduced data catalogs gained, and discusses common and differing approaches and the lessons that can be learned from their application.
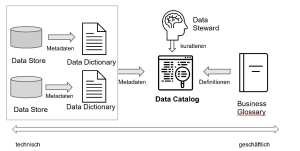
The importance of data catalogs
Data catalogs can do a lot in terms of making a company’s data transparent and accessible – and also getting people to trust it. Data catalogs serve as a central tool for obtaining information about data, including metadata and data origins and quality. By providing an integrated overview of a company’s data landscape, data catalogs make it possible for users to improve their knowledge about existing data and how to use it. In addition, data catalogs form the foundation for effective data quality initiatives. The biggest benefit offered by a data catalog is increased transparency with regard to existing data assets, which is very important, particularly in these times of digitalization and the increasing significance of data evaluation.
Challenges associated with the introduction of data catalogs
Introducing a data catalog involves several challenges with regard to technical complexity, integration into existing business processes, and ensuring a high level of data quality. Technical implementation requires extensive knowledge about the existing IT infrastructure and the data landscape. In addition, it is very important to incorporate the company’s business logic into the implementation process so as to ensure that the data catalog effectively supports the given business requirements. Another critical element is data quality, as the ability to enjoy the benefits of a data catalog depends directly on the accuracy and reliability of the information such a catalog contains.
Practical experience at six companies
Various motives, strategies, factors of success, and lessons were identified on the basis of interviews with staff from six companies that have already created data catalogs. In the interviews, these companies emphasized the value data catalogs were able to create for them in terms of transparency, data quality, user friendliness, and governance. An iterative approach was often chosen for the implementation process in order to efficiently address problems such as data silos and a lack of data quality. Support from management and the presentation of the practical benefits offered by the data catalog were also cited as essential preconditions for a successful introduction.
Commonalities and differences in the approaches
Despite the individual differences between the different companies’ needs and strategies, several common factors of success were identified. These include the significance of metadata, step-by-step implementation, and user friendliness. Differences were discovered mainly with regard to specific requirements, governance practices, and technology integration. These findings underscore the fact that there is no single approach for introducing a data catalog; instead, success here depends on adapting to the specific conditions and challenges at a company.
Conclusion and outlook
Data catalogs are a powerful tool that companies can employ to effectively manage and utilize their data records and assets. The experience gained and lessons learned by companies that have successfully introduced data catalogs offer valuable insights into the best strategies and practices. It is clear that successful implementation of a data catalog requires careful planning, support from management, and adjustments in line with a company’s specific needs. Future workstreams could further examine the detailed skills and trends associated with data catalog technology in order to help companies use and manage their data records and assets more effectively.
 Deutsch
Deutsch  English
English